Sicilian language
| Sicilian | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sicilianu | ||
| Spoken in | ||
| Total speakers | est. 8 million (Gordon, 2005) | |
| Ranking | 60-70 | |
| Language family | Indo-European | |
| Language codes | ||
| ISO 639-1 | None | |
| ISO 639-2 | scn | |
| ISO 639-3 | scn | |
| Linguasphere | ||
 |
||
| Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols in Unicode. | ||
Sicilian (lu sicilianu, Italian: lingua siciliana, also known as Siculu or Calabro-Sicilian) is a Romance language. Its dialects make up the Italiano Meridionale-estremo language group, which are spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands; in southern and central Calabria (where it is called Southern Calabro); in the southern parts of Apulia, the Salento (where it is known as Salentino); and Campania, on the Italian mainland, where it is called Cilentano (Gordon, 2005). Ethnologue (see below for more detail) describes Sicilian as being "distinct enough from Standard Italian to be considered a separate language" (Gordon). Some assert that Sicilian represents the oldest Romance language derived from Vulgar Latin (Privitera, 2004), but this is not a widely-held view amongst linguists. For instance, Cipolla describes such a view as radical (2004, p. 151).
Contents |
Speakers
It is currently spoken by the majority of the inhabitants of Sicily and by emigrant populations around the world. The latter are to be found in the countries which attracted large numbers of Sicilian immigrants during the course of the past century or so, especially the United States, Canada, Australia and Argentina. In the past two or three decades, large numbers of Sicilians were also attracted to the industrial zones of northern Italy and indeed the rest of the European Union, especially Germany.
Sicilian is not used as an official language anywhere, even within Sicily. There is currently no central body, in Sicily or elsewhere, that regulates the language in any way. However, the Center for Sicilian Philological and Linguistic Studies in Palermo has been researching and publishing information on the Sicilian language since its inception in 1951[1].
The autonomous regional parliament of Sicily has legislated to encourage the teaching of Sicilian at all schools, but inroads into the education system have been slow (Cipolla, 2004).
The language is officially recognized in the municipal statutes of Sicilian towns, such as Caltagirone[2] and Grammichele[3], in which the inalienable historical and cultural value of the Sicilian language is proclaimed. Further, the Sicilian language is to be protected and promoted under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML). However, the Italian Parliament has yet to ratify this draft law[4].
Ethnologue report on Sicilian
Other names
Alternate names of Sicilian are Calabro-Sicilian, Sicilianu, and Siculu. The term Calabro-Sicilian refers to the fact that a form of Sicilian, or a dialect closely related to Sicilian, is spoken in central and southern Calabria. Sicilianu is the name of the language in Sicilian itself (Gordon).
The term "Siculu" describes one of the larger prehistoric groups living in Sicily (the Sicels or Siculi) before the arrival of Greeks in the 8th century BC (see below). It can also be used as an adjective to qualify, or further elaborate on, the origins of a person, for example: Siculo-American (siculu-miricanu) or Siculo-Australian (Gordon).
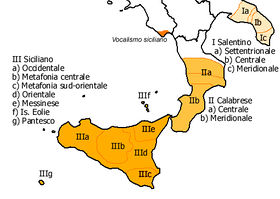
Dialects of Sicilian
As a language, Sicilian has its own dialects, in the following main groupings (Gordon and Bonner 2001):
- Western Sicilian (in Palermo, Trapani, Central-Western Agrigentino)
- Central Metafonetica (in the central part of Sicily that includes some areas of the Provinces of Caltanissetta, Messina, Enna, Palermo and Agrigento)
- Southeast Metafonetica (in the Province of Ragusa and the adjoining area within the Province of Syracuse)
- Ennese (in the province of Enna)
- Eastern Nonmetafonetica (in the area including the province of Catania, the second largest city in Sicily, and the adjoining area within the Province of Syracuse)
- Messinese (in the province of Messina)
- Isole Eolie (in the Aeolian Islands)
- Pantesco (on the island of Pantelleria)
- Southern and Central Calabrian (Calabrese) (in the southern and central sections of Calabria, including the provinces of Reggio Calabria, Vibo Valentia, Catanzaro and most of Crotone)
- Southern Apulian (Pugliese) (also called Salentino, and reportedly a dialect of Sicilian on the peninsular section of Apulia)
- Cilentano (In the Geographical region of Cilento in Campania)
Other observations
Sicilian is described as "vigorous" (in terms of not being in danger of extinction), although most Sicilians are described as being at least bilingual (being fluent in Italian as the official language of Italy). The strong French influence on Sicilian (elaborated below) raises the prospect that it may be better classified as a Southern Romance rather than Italo-Western language (Gordon).
History
Early influences
Because Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean and virtually all Mediterranean peoples have passed through it (Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Arabs, French, Aragonese, Spanish, Italians), Sicilian displays the rich and varied influence of several languages on its lexical stock and grammar. Such languages include Greek, Latin, Arabic, Norman, Lombard, Provençal, German, Catalan, French, Spanish and of course Italian, to say nothing of prehistoric influence from the island's pre-Indo-European settlers. The very earliest influences, visible in Sicilian to this day, exhibit both prehistoric Mediterranean elements and prehistoric Indo-European elements, and occasionally a blending of both (Giarizzo 1989 and Ruffino 2001).
Before the Roman conquest, Sicily was occupied by remnants of the indigenous populations (the Sicani, Elymi, Siculi, the third arriving between the second and first millennium BC), as well as by Phoenicians (from between the 10th and 8th centuries BC) and Greeks (from the 8th century BC). The Greek language influence remains strongly visible, while the influences from the other groups are less obvious. What can be stated with certainty is that there remain pre-Indo-European words in Sicilian of an ancient Mediterranean origin, but one cannot be more precise than that. Of the three main prehistoric groups, only the Siculi were Indo-European, and their speech is likely to have been closely related to that of the Romans (Ruffino).
The following table illustrates the difficulty linguists face in tackling the various sub-strata of the Sicilian language. The examples are for the English word "twins" (Ruffino).
| Stratum | Word | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modern | giameddi | Italian | gemelli |
| Medieval | bizzuni, vuzzuni | Norman | besson |
| binelli | Ligurian | beneli | |
| Ancient | èmmuli | Latin | gemulus |
| cucchi | Latin | copula | |
| minzuddi | Latin | medius | |
| ièmiddi, ièddimi | Greek | didymos | |
A similar qualifier can be applied to many of the words that appear in this article. Sometimes we may know that a particular word has a prehistoric derivation, but we do not know whether the Sicilians have inherited it directly from the indigenous populations, or whether it has come to them via another route. Similarly, we might know that a particular word has a Greek origin, but we do not know from which Greek period the Sicilians first used it (pre-Roman occupation or during its Byzantine period), or once again, whether the particular word may even have come to Sicily via another route. For instance, by the time the Romans had occupied Sicily during the 3rd century BC, the Latin language had made its own borrowings from Greek (Ruffino).
Pre-classical period
The words with a prehistoric Mediterranean derivation often refer to plants native to the Mediterranean region or to other natural features. Bearing in mind the qualifiers mentioned above (alternative sources are provided where known), examples of such words include:
- alastra (a thorny, prickly plant native to the Mediterranean region; but also Greek kelastron and may in fact have penetrated Sicilian via one of the Gallic idioms) (Ruffino)
- ammarrari (to dam or block a canal or running water; but also Spanish embarrar - to muddy) (Giarrizzo)
- calancuni (ripples caused by a fast running river)
- calanna (landslide of rocks)
- racioppu (stalk or stem, e.g. of a fruit, ancient Mediterranean word rak) (Giarrizzo)
- timpa (crag, cliff; but also Greek tymba, Latin tumba and Catalan timba) (Ruffino).
There are also Sicilian words with an ancient Indo-European origin that do not appear to have come to the language via any of the major language groups normally associated with Sicilian, i.e. they have been independently derived from a very early Indo-European source. The Siculi are a possible source of such words, but there is also the possibility of a cross-over between ancient Mediterranean words and introduced Indo-European forms. Some examples of Sicilian words with an ancient Indo-European origin:
- dudda (mulberry; similar to Welsh rhudd meaning the colour "pink"; Romanian dudă) (Giarrizzo)
- scrozzu (not well developed; similar to Lithuanian su-skurdes with a similar meaning and Old High German scurz, meaning short) (Giarrizzo)
- sfunnacata (multitude, vast number; from Indo-European und / fund meaning water) (Giarrizzo).
Greek influences
The following Sicilian words are of a Greek origin (including some examples where it is unclear whether the word is derived directly from Greek, or via Latin):
- appizzari - to rot, go bad (as in fruit), ruin (from (eks) èpeson), (Giarrizzo)
- babbiari - to fool around (from babazo, which also gives the sicilian words: babbazzu and babbu - stupid; but Latin babulus and Spanish babieca)
- bucali - pitcher (from baukalion), (Giarrizzo)
- bùmmulu - water receptacle (from bombylos; but Latin bombyla), (Ruffino)
- cartedda - basket (from kartallos; but Latin cratellum), (Ruffino)
- carusu - boy (from kouros; but Latin carus - dear, Sanskrit caruh - amiable)
- casèntaru - earthworm (from gas enteron), (Giarrizzo)
- cirasa - cherry (from kerasos; but Latin cerasum), (Giarrizzo)
- cona - icon, image, metaphor (from eikon; but Latin icona), (Ruffino)
- cuddura - type of bread (from kollyra; but Latin collyra), (Ruffino)
- grasta - flower pot (from gastra; but Latin gastra), (Ruffino)
- naca - cradle (from nake), (Giarrizzo)
- ntamari - to stun, amaze (from thambeo; but Calabrian (Calabrese) tammaru - stupid, comes from Arabic tammar date vendor), (Giarrizzo)
- pistiari - to eat (from apestiein), (Giarrizzo)
- tuppiàri - to knock (from typto), (Giarrizzo).
Vulgar Latin was spoken by the Roman occupation troops who garrisoned Sicily after Rome annexed the island (after the end of the First Punic War, ca. 261 BC). A historical feature shared by Sicily, the far south of Calabria, and the province of Lecce, is that during the Roman period, these areas were never completely Latinised. Greek remained the main language for the majority of the population. This helps explain the linguistic differences in these areas and those immediately to the north which were, more or less, Latinised (Hull). It is also why Sicilian is often referred to as a neo-Latin language – it did not descend directly from Latin (although some linguists disagree with that view, see below).
From 476 to 535 AD, the Ostrogothic kingdom ruled Sicily, although their presence did not impact the Sicilian language (Ruffino). The few Germanic influences to be found in Sicilian do not appear to originate from this period. One exception might be abbanniari or vanniari (to hawk goods, proclaim publicly) from Gothic bandujan - to give a signal. Also possible is schimmenti (diagonal) from Gothic slimbs (slanting). Other sources of Germanic influences include the Hohenstaufen rule of the 13th century, words of Nordic and Germanic origin contained within the speech of 11th century Norman and Lombard settlers, and the short period of Austrian rule in the 18th century.
Arab period
In 535 AD, Emperor Justinian I made Sicily a Byzantine province, and for the second time in Sicilian history, the Greek language became a familiar sound across the island (Hull, 1989). As the power of the Byzantine Empire waned, Sicily was progressively conquered by Saracens from North Africa, from the mid 9th to mid 10th centuries. The Arabic language influence is noticeable in around 300 Sicilian words, most of which relate to agriculture and related activities (Hull and Ruffino). This is understandable since the Saracens introduced to Sicily the most then-modern irrigation and farming techniques and a new range of crops – nearly all of which remain endemic to the island to this day.
Some words of Arabic origin:
- azzizzari - to embellish (from aziz; precious, beautiful), (Giarrizzo)
- babbaluciu - snail (from babus; but Greek boubalàkion), (Giarrizzo)
- burnia - jar (from burniya; but Latin hirnea), (Giarrizzo)
- cafisu - measure for liquids (from qafiz), (Giarrizzo)
- cassata - sicilian ricotta cake (from qashatah; but Latin caseata - something made from cheese), (Giarrizzo)
- gèbbia - artificial pond to store water for irrigation (from gabiya), (Giarrizzo)
- giuggiulena - sesame seed (from giulgiulan), (Giarrizzo)
- mafia - swagger or boldness/bravado (from mahyas "aggressive boasting, bragging", or from marfud "rejected")[5]
- ràisi - leader (from rais), (Giarrizzo)
- saia - canal (from saqiya), (Giarrizzo)
- zaffarana - saffron, type of plant whose flowers are used for medicinal purposes and in Sicilian cooking (from safara)
- zagara - blossom (from zahar)
- zibbibbu - type of grape (from zabib), (Giarrizzo)
- zuccu - tree trunk (from suq; but Aragonese soccu and Spanish zoque), (Giarrizzo).
Throughout the Arab epoch of Sicilian history, a large Greek-speaking population remained on the island and continued to use the Greek language, or most certainly a variant of Greek heavily influenced by Arabic (Hull). What is less clear is the extent to which a Latin-speaking population survived on the island. While a form of Vulgar Latin clearly survived in isolated communities during the Arab epoch, there is much debate as to the influence it had (if any) on the development of the Sicilian language, following the re-Latinisation of Sicily (discussed in the next section). There are few Sicilian words reflecting an archaic Latin form (as may be found, for example, in Sardinian), so the influence may have been minor (Hull). However, some forms do exist, so the tantalising prospect of a Sicilian form of a Vulgar Latin surviving the Arab period and influencing the modern development of Sicilian remains open (as already mentioned, Privitera puts forward the radical proposition that medieval Sicilian descends directly from a form of Vulgar Latin that survived throughout the Byzantine and Arab periods).
These are some words of Latin origin that may have survived the Arab epoch:
- antura - a while ago (from ante oram - an hour ago), (Giarrizzo)
- asciari - to find (from afflare, cf. Spanish "hallar", to find), (Giarrizzo)
- bìfara - to fruit twice yearly, Large-green fig (from bifera), (Giarrizzo)
- filìnia - cobweb (from filum, line, strand), (Giarrizzo)
- oggiallanu or ovannu - last year (from hodie est annus).
Linguistic development from the middle ages
By 1000 AD the whole of what is today southern Italy, including Sicily, was a complex mix of small states and principalities, languages and religions (Hull). The whole of Sicily was controlled by Muslim Saracens, although there remained a large Greek speaking and Christian population. The far south of the Italian peninsula was part of the Byzantine empire and predominantly Greek speaking, although many communities were reasonably independent of Constantinople. The principality of Salerno was controlled by Lombards (or Langobards) who had also started to make some incursions into Byzantine territory and had managed to establish some isolated independent city-states (Norwich 1992). It was into this mix that the Normans thrust themselves in ever increasing numbers during the first half of the 11th century.
Norman French influence
When the two most famous of southern Italy's Norman adventurers, Roger of Hauteville and his brother, Robert Guiscard, began their conquest of Sicily in 1061, they already controlled the far south of Italy (Apulia and Calabria). It took Roger 30 years to complete the conquest of Sicily (Robert died in 1085), (Norwich). In the process, the re-Latinisation and re-Christianisation of Sicily had begun. A long list of Norman words were to become absorbed by the new language during this period, for example:
- accattari - to buy (from Norman acater, Modern French acheter), (Ruffino)
- ammuntuari/ammuntuvari – to mention, nominate (from Norman mentevoir), (Giarrizzo)
- appujari - to support (from modern French "appuyer") (Pietrocola)
- bucceri (vucceri) - butcher (from bouchier), (Hull)
- custureri - tailor (from coustrier; Modern French couturier), (Hull)
- firranti - grey (from ferrant), (Giarrizzo)
- foddi - mad (from fol; Modern French fou / fol / folle), (Hull)
- giugnettu - July (from juignet; Modern French juillet), (Hull)
- ladiu or laiu - ugly (from laid), (Hull)
- largasìa - generosity (from largesse), (Giarrizzo)
- puseri - thumb (from poucier), (Hull)
- racina - grape (from raisin), (Hull)
- raggia – anger (from rage), (Giarrizzo)
- sbernu/a - alder tree (from verna or vernon), Gallic-Norman, may be from Osbern or Asbern.
- travagghiari - to work (from French "travailler") (Pietrocola)
- testa - head (from teste), (Hull)
- trippari - to hop, skip (from Norman triper), (Giarrizzo).
The following factors that emerged during or immediately after the conquest were to prove critical in the formation of the Sicilian language:
- The Normans brought with them not only their own Norman-speaking kin (more than likely in quite small numbers), but mercenaries from mainland Italy. In particular, these included Lombards (with their Gallo-Italic idiom, Lombardic, ancestral to the modern Lombard language) and other Italians from around Campania. The latter would bring with them the Vulgar Latin from that region, an idiom not too different from that to be found in central Italy at the time (Hull).
- The thirty-year-long war of conquest and the encouragement given to re-establishing Christianity resulted in the depopulation of Saracens in most parts of Sicily, many of whom escaped to North Africa (Hull, 1989 and Norwich).
- Further migrations to settle the depopulated areas were encouraged from the mainland by Roger, in particular, Italian settlers from areas controlled by the Roman Catholic Church. The western parts of Sicily were colonised by migrants from Campania, and the central-eastern parts by settlers from the western Padan Plain (a.k.a. Po River Valley) in northern Italy who also brought with them a Gallo-Italic idiom. After the death of Roger I, and under the regency of Adelaide del Vasto during the minority of her son, Roger II (herself from northern Italy), this process of Lombardic colonisation was intensified (Hull and Norwich).
We can see above the main factors that go into framing the Sicilian language as we know it today. The Vulgar Latin base (predominantly from Campania) was similar to the Vulgar Latin in central Italy (and therefore, by implication, reasonably similar to the Vulgar Latin in Tuscany that would eventually form the base for the national language). This base from Campania was influenced by the many Gallic influences present in Sicily at the time, namely Norman, French and Langobardic. Underneath that were remnants of the Arabic and Greek idioms that the new language eventually replaced, but hundreds of words remained in the vocabulary of the changing Romance language.
Other Gallic influences
The Lombard influence is of particular interest. Even to the present day, a Gallo-siculo dialect exists in the areas where the Lombard colonies were the strongest, namely Novara, Nicosia, Sperlinga, Aidone and Piazza Armerina (Hull). The Siculo-Gallic dialect did not survive in other major Lombard colonies, such as Randazzo, Bronte and Paternò (although they did influence the local Sicilian vernacular). The Gallo-Italic influence was also felt on the Sicilian language itself, as follows (Hull):
- sòggiru - father-in-law (from suoxer)
- cugnatu - brother-in-law (from cognau)
- figghiozzu - godson (from figlioz)
- orbu and orvu - blind (from orb)
- arricintari - to rinse (from rexentar)
- unni - where (from ond)
- the names of the days of the week:
- luni - Monday (from lunes)
- marti - Tuesday (from martes)
- mèrcuri - Wednesday (from mèrcor)
- jovi - Thursday (from juovia)
- vènniri - Friday (from vènner)
The origins of another Gallic influence, that of Old Provençal, had three possible sources.
- As mentioned above, the number of actual Normans in Sicily are unlikely to have ever numbered much higher than 5,000 at any time. Their numbers were boosted by mercenaries from southern Italy, but it is also possible that mercenaries came from as far away as southern France. The Normans made San Fratello a garrison town in the early years of the occupation of the north-eastern corner of Sicily. To this day (in ever decreasing numbers) a Siculo-Gallic dialect is spoken in San Fratello that is clearly influenced by Old Provençal, leading one to the conclusion that a significant number in the garrison came from that part of France (Privitera 2001). This may well explain the dialect spoken only in San Fratello, but it does not wholly explain the diffusion of many Provençal words into the Sicilian language. On that point we are confronted with a further two possibilities.
- Some Provençal words may have entered the language during the regency of Margaret of Navarre between 1166 and 1171 when her son, William II of Sicily, succeeded to the throne at the age of 12. The Queen's closest advisers, entourage and administrators were from the south of France (Norwich), and many Provençal words entered the language during this period.
- The Sicilian School of poetry (discussed below) was strongly influenced by the Provençal of the troubadour tradition (Cipolla 2004 p. 141). This element is deeply embedded in Sicilian culture, for example, the tradition of Sicilian puppetry (opira dî puppi) and the tradition of the cantastorii (literally sing stories). There is no doubt that Provençal troubadours were active during the reign of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, and that some Provençal words would have passed into the Sicilian language via this route.
Some examples of Sicilian words derived from Provençal:
- addumari - to light (from allumar); but also "to turn sthg. on"
- aggrifari - to kidnap, abduct (from grifar), (Giarrizzo)
- banna – side, place (from banda), (Giarrizzo)
- burgisi - landowners, citizens (from borges)
- lascu - sparse, thin, infrequent (from lasc), (Giarrizzo)
- lavanca and allavanca - precipice (from lavanca), (Giarrizzo)
- paraggiu - equal (from paratge), (Giarrizzo)
Sicilian School of Poetry
It was during the reign of Frederick II (or Frederick I of Sicily) between 1198 and 1250, with his patronage of the Sicilian School of poetry, that Sicilian became the first of the Italic idioms to be used as a literary language (Cipolla 2004 p. 141). The influence of the school, and the use of Sicilian itself as a poetic language, was acknowledged by the two great Tuscan writers of the early Renaissance period Dante and Petrarch. The influence of the Sicilian language should not be underestimated in the eventual formulation of a lingua franca that was to become modern Italian. The victory of the Angevin army over the Sicilians at Benevento in 1266 not only marked the end of the 136-year Norman-Swabian reign in Sicily, it effectively ensured that the centre of literary influence would eventually move from Sicily to Tuscany (Cipolla 2004 p. 141). While Sicilian, as both an official and literary language would continue to exist for another two centuries, the language would soon follow the fortunes of the kingdom itself in terms of prestige and influence.
As a side note, there are some Germanic influences in the Sicilian language, and many of these date back to the time of the Swabian kings (amongst whom Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor enjoyed the longest reign). Words that probably originate from this era include:
- arbitriari - to work in the fields (from arbeit), (Giarrizzo)
- vardari - to watch over (from wartên), (Giarrizzo)
- guastari or vastari - to waste, use up (from wastjan)
- guddefi - forest, woods (from wald, note resemblance to Anglo-Saxon wudu), (Giarrizzo)
- guzzuniari - to wag, as in a tail (from hutsen), (Giarrizzo)
- lancedda - terracotta jug for holding water (from Old High German lagella), (Giarrizzo)
- salaguni - willow (from Old High German salaha)
- sparagnari - to save money (from Old High German sparen), (Giarrizzo).
Catalan influence
Following the Sicilian Vespers of 1282, the kingdom was to come under the influence of the Kingdom of Aragon (Runciman 1958), and as a result, the Catalan language (and the closely related Aragonese) would add a new layer of vocabulary in the succeeding century. For the whole of the 14th century, both Catalan and Sicilian were the official languages of the royal court (Hughes 1993). Sicilian was also used to record the proceedings of the parliament of Sicily (one of the oldest parliaments in Europe) and for other official purposes (Cipolla 2004, p. 155). While it is often difficult to determine whether a word has come to us directly from Catalan (as opposed to Provençal or Spanish), the following are likely to be such examples:
- accabbari - to finish, end (from acabar)
- addunarisi - to notice, realise (from adonar-se), (Giarrizzo)
- affruntarisi - to be embarrassed (from afrontar-se), (Giarrizzo)
- ammucciari - to hide (from amagar)
- arruciari – to moisten, soak (from arruixar), (Giarrizzo)
- criscimogna - growth, development (from creiximoni), (Giarrizzo)
- muccaturi - handkerchief (from mocador)
- nzirtari - to guess (from encertar)
- priàrisi - to be pleased (from prear-se), (Giarrizzo)
- taliàri - to look at somebody/something. (from talaiar; but Arab tali'a).
Spanish period to the modern age
By the time the Aragonese crown was joined with the Spanish realm in the late 15th century, the Italianisation of written Sicilian in the parliamentary and court records had commenced. By 1543 this process was virtually complete, with the Tuscan dialect of Italian becoming the lingua franca of the Italian peninsula and supplanting written Sicilian (Cipolla 2004 p. 155).
Spanish rule had hastened this process in two important ways:
- Unlike the Aragonese, almost immediately the Spanish placed viceroys on the Sicilian throne. In a sense, the diminishing prestige of the Sicilian kingdom reflected the decline of Sicilian from an official, written language to eventually a spoken language amongst predominantly illiterates.
- The expulsion of all Jews from Spanish dominions ca. 1492 altered the population of Sicily. Not only did the population decline, many of whom were involved in important industries, but some of these Jewish families had been in Sicily for around 1,500 years, and Sicilian was their mother tongue which they used in their schools. Thus the seeds of a possible broad-based education system utilising books written in Sicilian was lost.
Spanish rule lasted over three centuries (not counting the Aragonese and Bourbon periods on either side) and had a significant influence on the Sicilian vocabulary. The following words are of Spanish derivation:
- arricugghirisi - to return home; (from arrecogerse; but Catalan recollir-se)
- balanza – scales (from balanza), (Giarrizzo)
- fileccia - arrow (from flecha), (Giarrizzo)
- làstima – lament, annoyance (from lástima), (Giarrizzo)
- pignata – pan (from pinada)
- pinzèddu – brush (from pincel), (Giarrizzo)
- ricivu – receipt (from recibo), (Giarrizzo)
- spagnari - to be frightened ( cross over of Sic. appagnari with Sp. espantarse), (Giarrizzo)
- spatari - to impede or disarm someone of his sword (from espadar), (Giarrizzo)
- sulità or sulitati – solitude (from soledad), (Giarrizzo).
Since the Italian Unification (the Risorgimento of 1860–1861), the Sicilian language has been significantly influenced by (Tuscan) Italian. This process has quickened since World War II due to improving educational standards and the impact of mass media, such that increasingly, even within the family home, Sicilian is not necessarily the language of choice. The Sicilian Regional Parliament recently voted to make the teaching of Sicilian a part of the school curriculum at primary school level, but as of 2007 only a fraction of schools teach Sicilian. There is also little in the way of mass media offered in Sicilian. The combination of these factors means that the Sicilian language continues to adopt Italian vocabulary and grammatical forms to such an extent that many Sicilians themselves cannot distinguish between correct and incorrect Sicilian language usage.
Distinguishing features of Sicilian
Unique sounds
Sicilian has a number of consonant sounds which, if not unique to Sicilian, certainly set it apart from the other major Romance languages. The most unusual sounds include, but are not limited to, the retroflex consonants or cacuminals (Cipolla 2005).
- DD — The -ll- sound (in words of Latin origin, for example) manifests itself in Sicilian as a voiced retroflex plosive with the tip of the tongue curled up and back, a sound which is not part of standard (Tuscan) Italian. In standard literary Sicilian, this sound is written simply as -dd- (but can also be found written ḍḍ, ddh or ddr). The sound itself is not [d] but rather [ɖ]. For example, the Italian word bello [ˈbɛllo] is beddu [ˈbɛɖɖu] in Sicilian. For comparison, this sound is somewhat like the 'r' sound in Japanese.
- DR, TR — Similarly, Sicilian has a unique pronunciation of the digraphs -tr- and -dr- not common to Italian. The sound of -tr- is exactly like that heard in English tree and the sound of -dr- exactly like the digraph heard in English dragon.
- RR — The Sicilian consonant cluster -rr- also differs from Italian in that it is a voiced postalveolar fricative ([ʒ] according to IPA notation). At the beginning of a word, the single letter -r- is similarly always pronounced double, though this is not indicated orthographically. Therefore, the -rr- sound heard in the words riccu and terra is similar to the 'sh' sound in English vision or the 'j' sound in French jour. This phenomenon, however, does not include words that include an 'r' resulting from rhotacism (renti from denti) or assimilation (ranni from granni).
- STR — The trigraph -str- in Sicilian is quite different from the Italian form of the trigraph. The t is not pronounced at all and there is a faint whistle between the s and the r, the latter not being trilled as would be the case in Italian (Cipolla 2005). An example of this trigraph is the shr sound heard in English shred.
- Latin FL — The other unique Sicilian sound is found in those words that have been derived from Latin words containing -fl-. This has generally become fi in Italian, for example, fiume from Latin flumen (river). In standard literary Sicilian, the sound is rendered as ci (representing the voiceless palatal fricative [ç]), e.g. ciumi or /çjumi/, (but can also be found in written form as hi, sci, x or çi). The sound approximates to an allophone of English language /h/ before /ju/ as in words like huge, but slightly more fricative (Cipolla 2005).
- Sicilian Vowel System — One obvious difference from Italian is what linguists describe as the Sicilian Vowel System. Unlike the seven vowels shared by Italian, Vulgar Latin, and many other Romance languages, the Sicilian Vowel System only includes five: a [a], è [ɛ], i [i], ò [ɔ], u [u]. This results in the unstressed vowel o of Latin becoming an unstressed u in Sicilian (Hull). This causes the vowel u to have a far greater presence than the vowel o in Sicilian, while the opposite is true of other Romance languages such as Spanish and Italian (notwithstanding the conservative nature of Sicilian which retains the vowel u of the Latin stems -us and -um). Likewise, the unstressed vowel e of Latin becomes unstressed vowel i in Sicilian. As a result, the vowel i has a much greater presence than vowel e in Sicilian. In addition, one will never find a Sicilian word ending in the unaccented vowels e or o, with the exception of monosyllabic conjunctions. Due to the influence of Italian in the media post-World War II, as well as the recent influx of English terminology related to technology and globalization, there is an increasing number of words entering the Sicilian lexicon that do not adhere to the Sicilian Vowel System. However, the future of these borrowings is uncertain as Sicilian has always Sicilianized foreign loanwords over time in the past.
- Consonantal Palatalization — A further range of consonantal sound shifts occurred between the Vulgar Latin introduced to the island following Norman rule and the subsequent development of the Sicilian language. These sound shifts include: Latin -nd- to Sicilian -nn-; Latin -mb- to Sicilian -mm-; Latin -pl- to Sicilian -chi-; and Latin -li- to Sicilian -gghi- Pitrè 1875.
Gemination and contractions
Rarely indicated in writing, spoken Sicilian exhibits syntactic doubling or raddoppiamento (Cipolla 2005), which means that the first consonant of a word is lengthened when it is preceded by a vowel in the preceding word, e.g. è bonu [eˈbːonu]. This process of lengthening is also called gemination, which is a general term used for the lengthening of any sound.
The letter j at the start of a word can have three separate sounds, depending on what precedes the word (Cipolla 2005). For instance, in jornu (day), the j is pronounced [j] as in English y, [ˈjoɾnu]. However, after a nasal consonant, it is pronounced [dʒ] as in un jornu, [unˈdʒoɾnu] (which English speakers might spell as "unjornu", with the j sound in "jelly"). Tri jorna (three days) is pronounced [triˈgjoɾna], the j becoming [ɡj] (like English gu in "ague"), after a vowel.
Another difference between the written and spoken languages is the extent to which contractions will occur in everyday speech. Thus a common expression such as avemu a accattari... (we have to go and buy...) will generally be reduced to amâ 'ccattari when talking to family and friends (Bonner).
The circumflex is commonly used in denoting a wide range of contractions in the written language, in particular, the joining of simple prepositions and the definite article. Examples: di lu = dû (of the), a lu = ô (to the), pi lu = pû (for the), nta lu = ntô (in the), etc. (Bonner).
Gender and the formation of plurals
Generally speaking, Sicilian has the same ending for feminine nouns (and their adjectives) as does Italian, that being the [a], for example: casa (house), porta (door), carta (paper), but there are exceptions to this rule, for example, soru (sister), ficu (fig). Whereas Italian uses [o] as the ending for masculine nouns, Sicilian generally uses [u], for example: omu (man), libbru (book), nomu (name). The ending i can be either masculine or feminine, as in Italian the ending e can be of either gender.
Unlike Italian, Sicilian uses one letter, i, to denote the plural for both masculine and feminine nouns, for example: casi (houses), porti (doors), tauli (tables). There are also many exceptions to this rule which are not always shared by Italian, for example: òmini (men), libbra (books), jorna (days), jòcura (games), manu (hand/hands), vrazza (arms), jardina (gardens), scrittura (writers), signa (signs), etc. (Bonner).
Omission of initial Latin "i"
In the vast majority of instances where the originating Latin word has had an initial "i", the Sicilian has dropped it completely. This can also happen occasionally where there was once an initial "e", and to a lesser extent "a" and "o". Examples: mpurtanti (important), gnuranti (ignorant), nimicu (enemy), ntirissanti (interesting), llustrari (to illustrate), mmàggini (image), cona (icon), miricanu (American), etc. (Camilleri 1998).
Verb "to have"
Unlike Italian, Sicilian only has one auxiliary verb, aviri, to have. This is a characteristic that it shares with Catalan and Romanian. Sicilian also uses the verb "to have" to denote obligation (as is used in languages like English, German, Neapolitan and in Spanish, which uses the respective verb tener, though in formal —mainly written— language haber is still used). For example: avi a jiri (pronounced [ˈaviaˈɡːiɾi] — English: "[he/she] has to go"; German: "[er/sie] hat zu gehen"; Spanish: tiene que ir or ha de ir). As also occurs in German and Spanish, a preposition is required before the verb in this specific construction.
The verb "aviri" is also used to form the future tense in Sicilian, as it no longer has a Simple Future construction. This is an ancient feature, also found in Sardinian. For example: avi a cantari (pronounced [ˈaviakːanˈtaɾi] or [ˈawakːanˈdaɾi] depending on dialects) — English: "[he/she] will sing" (Bonner).
Verb "to go"
Like French, Spanish, and English, but unlike Italian, Sicilian may use the verb jiri, to go, to signify the act of being about to do something. Italian does not use the verb andare, to go, in this way. For example: vaiu a cantari (pronounced [ˈvaiuakːanˈtaɾi]), in English "I'm going to sing" or, literally, "I go to sing." In this way, jiri + a + infinitive can also be a way to form the simple future construction (Bonner)..
Tenses and moods
The main conjugations in Sicilian are illustrated below with the verb èssiri, "to be" (Pitrè 1875).
| Infinitive | èssiri / siri | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gerund | essennu / sennu | |||||
| Past participle | statu | |||||
| Indicative | ju | tu | iddu | nuàutri | vuàutri | iddi |
| Present | sugnu | sì | esti / è | semu | siti | sunnu / sù |
| Imperfect | era | eri | era | èramu | èravu | èranu |
| Preterite | fui | fusti | fu | fomu | fùstivu | foru |
| Future¹ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Conditional² | ju | tu | iddu | nuàutri | vuàutri | iddi |
| fora | fori | fora | fòramu | fòravu | fòranu | |
| Subjunctive | ju | tu | iddu | nuàutri | vuàutri | iddi |
| Present | sia | si'/fussi | sia | siamu | siati | sianu |
| Imperfect | fussi | fussi | fussi | fùssimu | fùssivu | fùssiru |
| Imperative | tu | vassìa³ | vuàutri | |||
| sì | fussi | siti | ||||
1. The Simple Future tense in Sicilian is no longer in use. However the Sicilian language employs several possible methods of expressing the future tense:
- 1) by simply using the present indicative, usually preceded by an adverb of time:
- Stasira vaiu ô tiatru — This evening I [will] go to the theatre; or, using a similar English construction, This evening I am going to the theatre
- Dumani ti scrivu — Tomorrow I [will] write to you.
- 2) by using a compound form consisting of the appropriate conjugation of aviri a ("have to") in combination with the infinitive form of the verb in question:
- Stasira haju a gghìri/ìri ô tiatru — This evening I will [/must] go to the theatre.
- Dumani t'haju a scrìviri — Tomorrow I will [/must] write to you.
- In speech the contracted forms of aviri often come into play:
- haju a → /hâ/hê; hai a → hâ, havi a → havâ, avemu a → hamâ; aviti a → hatâ
- Dumani t'hâ scrìviri — Tomorrow I will [/must] write to you (Bonner).
2. The Conditional tense has also fallen into disuse. The Conditional has two tenses:
- 1) The Present Conditional tense, which is replaced by either:
- i) the Present Indicative:
- Cci chiamu si tu mi duni lu sò nùmmaru — I [would] call her if you [would] give me her number, or
- ii) the Imperfect Subjunctive:
- Cci chiamassi si tu mi dassi lu sò nùmmaru — I'd call her if you would give me her number; and
- i) the Present Indicative:
- 2) the Past Conditional tense, which is replaced by the Past Perfect Subjunctive:
-
- Cci avissi jutu si tu m'avissi dittu [/diciutu] unni esti / e' — I'd have gone if you would have told me where it is.
-
- Note that in a hypothetical statement, both tenses are replaced by the Imperfect and Past Perfect of the Subjunctive:
-
- Si fussi riccu m'accattassi nu palazzu — If I were rich I would buy a palace.
- S'avissi travagghiatu nun avissi patutu la misèria — If I had worked I wouldn't have suffered the misery (Bonner 2001).
-
3. The 2nd person singular (polite) of the Imperative does not follow the same pattern as the rest of the tense. The 2nd person singular and plural employ the Present Indicative in place of the Imperative, while the 2nd person singular (polite), because of its formality, employs the Present Subjunctive, which makes it less of a command and more of a request.
Examples of the written language
A range of extracts are offered below to illustrate the written form of Sicilian over the last few centuries, starting with a translation of the Lord's Prayer (Bonner), through to extracts from three of Sicily's more celebrated poets: Antonio Veneziano, Giovanni Meli and Nino Martoglio. The Lord's Prayer is written with three variations: a standard literary form from the island of Sicily, a southern Calabrian literary form and a southern Apulian literary form.
Lu Patri Nostru
| Sicilian (Sicily) | Calabro-sicilian (southern Calabria) | Salentino (southern Apulia, around Lecce) | Italian | Latin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patri nostru, ca siti ntrô celu, | Patri nostru ca siti 'nto celu | Sire nesciu ca stai an cielu | Padre nostro, che sei nei cieli, | Pater noster, qui es in caelis, |
| Santificatu fussi lu Vostru nomu. | Fussi santificatu u nomu vostru. | Cu'bbessa santificatu lu nume tou. | Sia santificato il tuo nome. | Sanctificetur nomen tuum. |
| Viatu vinissi lu Vostru regnu. | Venissi prestu lu regnu vostru. | Cu'bbegna 'mprima lu regnu tou. | Venga il tuo regno. | Adveniat regnum tuum. |
| Fatta fussi la Vostra Vuluntati | Fussi sempri faciùta a Vuluntà Vostra | Cu'bbessa sempre fatta la Vuluntate toa | Sia fatta la tua volontà | Fiat voluntas tua |
| Comu ntrô celu accussì ntra terra. | Comu 'ndo celu cusì 'nta terra. | Comu an cielu cussì an terra. | Come in cielo così in terra. | Sicut in caelo et in terra. |
| Dàtini sta jurnata lu nostru panuzzu, | Ratandìllu sta jurnata u pani quotidianu, | Dànnilu osce lu pane quotidianu nesciu, | Dacci oggi il nostro pane quotidiano, | Panem nostrum quotidianum da nobis hodie, |
| E pirdunàtini li nostri piccati | E pirdunatindi i nostri piccati | E perdunanni li peccati nesci | E rimetti a noi i nostri debiti | Et dimitte nobis debita nostra |
| Accussì comu nuiàtri li pirdunemu ê nostri nìmici. | Cusì comu nui i rimentimu ê nemici nostri. | Cussì comu nui li rimentimu a li nemici nesci. | Come noi li rimettiamo ai nostri debitori. | Sicut et nos dimittimus debitoribus nostris. |
| E nun lassàtini cascari ntrâ tintazzioni, | E non 'ndi rassàti mi carimu ntâ tentazzioni, | E nu' lassare cu cadimu 'n tentazzione, | E non ci indurre in tentazione, | Et ne nos inducas in tentationem, |
| Ma scanzàtini dû Mali. | Ma levatindi r'avanzi u Mali. | Ma 'lléandenni te lu male. | Ma liberaci dal male. | Sed libera nos a malo. |
| Amen. | Amen. | Amen. | Amen. | Amen. |
Extract from Antonio Veneziano
Celia, Lib. 2
(ca. 1575–1580)
| Sicilian | Italian | English |
|---|---|---|
| Non è xhiamma ordinaria, no, la mia, | No, la mia non è fiamma ordinaria, | No, mine is no ordinary flame, |
| è xhiamma chi sul'iu tegnu e rizettu, | è una fiamma che sol'io possiedo e controllo, | it's a flame that only I possess and oversight, |
| xhiamma pura e celesti, ch'ardi 'n mia; | una fiamma pura e celeste che dientro di me cresce; | a pure celestial flame that in me grows; |
| per gran misteriu e cu stupendu effettu. | da un grande mistero e con stupendo effetto. | by a great mystery and with great effect. |
| Amuri, 'ntentu a fari idulatria, | l'Amore, desiderante d'adorare icone, | Love, wanting to worship idols, |
| s'ha novamenti sazerdoti elettu; | è diventato sacerdote un'altra volta; | has once again become a high priest; |
| tu, sculpita 'ntra st'alma, sìa la dia; | tu, sculpita dientro quest'anima, sei la dea; | you, sculpted in this soul, are the goddess; |
| sacrifiziu lu cori, ara stu pettu. | il mio cuore è la vittima, il mio seno è l'altare. | my heart is the victim, my breast is the altar. |
(sourced directly from Arba Sicula Volume II, 1980)
Extract from Giovanni Meli
Don Chisciotti e Sanciu Panza (Cantu quintu)
(~1790)
| Sicilian | English |
|---|---|
| Stracanciatu di notti soli jiri; | Disguised he roams at night alone; |
| S'ammuccia ntra purtuni e cantuneri; | Hiding in any nook and cranny; |
| cu vacabunni ci mustra piaciri; | he enjoys the company of vagabonds; |
| poi lu so sbiu sunnu li sumeri, | however, donkeys are his real diversion, |
| li pruteggi e li pigghia a ben vuliri, | he protects them and looks after all their needs, |
| li tratta pri parenti e amici veri; | treating them as real family and friends; |
| siccomu ancora è n'amicu viraci | since he remains a true friend |
| di li bizzarri, capricciusi e audaci. | of all who are bizarre, capricious and bold. |
Extract from Nino Martoglio
Briscula 'n Cumpagni
(~1900; trans: A game of Briscula amongst friends)
| Sicilian | Italian | English |
|---|---|---|
| — Càrricu, mancu? Cca cc'è 'n sei di spati!... | — Nemmeno un carico? Qui c'è un sei di spade!... | — A high card perhaps? Here's the six of spades!... |
| — E chi schifiu è, di sta manera? | — Ma che schifo, in questo modo? | — What is this rubbish you're playing? |
| Don Peppi Nnappa, d'accussì jucati? | Signor Peppe Nappa,[7] ma giocate così? | Who taught you to play this game? |
| — Misseri e sceccu ccu tutta 'a tistera, | — Messere e asino con tutti i finimenti, | — My dear gentlemen and donkeys with all your finery, |
| comu vi l'haju a diri, a vastunati, | come ve lo devo dire, forse a bastonate, | as I have repeatedly told you till I'm blue in the face, |
| ca mancu haju sali di salera! | che non ho nemmeno il sale per la saliera! | I ain't got nothing that's even worth a pinch a salt! |
Influences on the Italian language
As one of the most-spoken languages of Italy, Sicilian has notably influenced the Italian lexicon. In fact, there are several Sicilian words that are nowadays part of the Italian language; they usually refer to things closely associated to Sicilian culture, with some notable exceptions (Zingarelli 2007):
- arancino (from arancinu): arancino, a Sicilian cuisine specialty;
- canestrato (from 'ncannistratu): a cheese typical of Sicily;
- cannolo (from cannolu): cannolo, a Sicilian pastry;
- cannolicchio (from cannulicchiu): razor-clam;
- carnezzeria (from carnizzaria): butcher's shop;
- caruso (from carusu): boy;
- cassata: cassata, a Sicilian pastry;
- cirneco (from cirnecu): a small breed of dogs common in Sicily;
- cosca: a small group of criminals affiliated to the Sicilian mafia;
- curatolo (from curatulu): watchman in a farm, with a yearly contract;
- dammuso (from dammusu): stony habitation typical of the island of Pantelleria;
- intrallazzo (from 'ntrallazzu): illegal exchange of goods or favours, but in a wider sense also cheat, intrigue;
- marranzano (from marranzanu): Jew's harp;
- marrobbio (from marrubbiu): quick variation of sea level produced by a store of water in the coasts as a consequence of either wind action or an atmospheric depression;
- minchia: penis in its original meaning, but also stupid person, is also widely used as interjection to show either astonishment or rage;
- picciotto (from picciottu): young man, but also the lowest grade in the Mafia hierarchy;
- pizzino (from pizzinu): small piece of paper;
- pizzo (from pizzu): literally meaning beak in Sicilian, it is protection money paid to the Mafia; it comes from the saying fari vagnari a pizzu (to wet one's beak).
- quaquaraquà: person devoid of value, nonentity; (onomatopoeia?; "the duck wants a say")
- scasare (from scasari): to leave en masse (means literally to move home);
- stidda (it.: stella): lower Mafia organization.
Language situation today
Sicily
Sicilian is estimated to have millions of speakers. However, it remains very much a home language spoken among peers and close associates. The regional Italian dialect has encroached on Sicilian, most evidently in the speech of the younger generations.
Poets in Sicily sometimes write in Sicilian. However, most speakers (especially the youngest ones) are literate just in Italian, not Sicilian; this implies a poor knowledge of the written language in all its formal grammar and spelling rules, in contrast to a still-wide diffusion of informal spoken Sicilian in the island.
The education system does not support the language. Local universities do not carry courses in Sicilian, or where they do it is described as dialettologia, that is, the study of dialects.
Diaspora
Outside Sicily, there is an extensive diaspora living in several major cities across North and South America, as well as other parts of Europe and Australia. The Sicilian-language respectively is spoken to varying extents within families and communities, however has no recognized status nor programmes established to preserve the language. Most Sicilians abroad are bi- or trilingual with Standard Italian and/or the host country language, be it English, Spanish, French, or Portuguese.
Other words/phrases
Sicilian phrase = Italian translation (English translation)
- Fàciri na bedda fiùra = fare una bella figura (to make a good impression)
- Vinu = vino (wine)
- òmu = uomo (man)
- fìmmina = donna (woman)
- dabbanna = l'altra parte (The other side)
- docu = lì (There)
- vussìa = Lei (you -polite form-)
- Accura! = Stai attento! (Be careful!)
- Iddu = lui (him/he)
- Idda = lei (her/she)
- Cu paja prima, pistia li pisci fitusi = chi paga prima, mangia il pesce puzzolente (he who pays before seeing the goods gets cheated)
See also
- Sicily
- Sicilian School
- Siculo-Arabic
- Sicilian Vowel System
Notes
- ↑ Centro di studi filologici e linguistici siciliani (CSFLS)
- ↑ Gazzetta Ufficiale della Regione Siciliana: Statuto del Comune di Caltagirone
- ↑ Gazzetta Ufficiale della Regione Siciliana: Statuto del Comune di Grammichele
- ↑ Cardi, Valeria. Italy moves closer to ratification of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. Eurolang. December 12, 2007
- ↑ This etymology is based on the books Mafioso by Gaia Servadio; The Sicilian Mafia by Diego Gambetta; and Cosa Nostra by John Dickie
- ↑ This collection of Giovanni Meli's poetry was edited and translated by Prof. Gaetano Cipolla.
- ↑ Peppe Nappa is a character of the Commedia dell'arte, similar to Pulcinella o Arlecchino.
- ↑ This collection of Nino Martoglio's poetry was edited and translated by Prof. Gaetano Cipolla.
References
- Arba Sicula Volume II, 1980 (bilingual: Sicilian and English)
- Bonner, J. K. "Kirk" (2001). Introduction to Sicilian Grammar. Legas. ISBN 1-88190141-6.
- Camilleri, Salvatore (2098). Vocabolario Italiano Siciliano. Edizioni Greco.
- Centro di Studi Filologici e Linguistici Siciliani (1977–2002) Vocabolario Siciliano, 5 volumi a cura di Giorgio Piccitto, Catania-Palermo (the orthography used in this article is substantially based on the Piccitto volumes).
- Cipolla, Gaetano (2004). "U sicilianu è na lingua o un dialettu? / Is Sicilian a Language?". Arba Sicula XXV (1&2): 138–175.
- Cipolla, Gaetano (2005). The Sounds of Sicilian. Legas. ISBN 188190151-3.
- Giarrizzo, Salvatore (1989). Dizionario Etimologico Siciliano. Herbita Editrice.
- Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.) (2005). "Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition". Sicilian: A language of Italy. Ethnologue. http://www.ethnologue.com/. Retrieved 2008-01-09.
- Hughes, Robert (1993). Barcelona. Harvill. ISBN 0-00-272167-8.
- Hull, Geoffrey (2001). Polyglot Italy: Languages, Dialects, Peoples. Legas. ISBN 0-949919-61-6.
- Martoglio, Nino (1993). The Poetry of Nino Martoglio. Legas. ISBN 1-881901-03-3. (bilingual: Sicilian and English; edited and translated by Prof. Gaetano Cipolla)
- Meli, Giovanni (1995). Moral Fables and other poems. Legas. ISBN 1-881901-07-6. (bilingual: Sicilian and English; edited and translated by Prof. Gaetano Cipolla)
- Norwich, John Julius (1992). The Kingdom in the Sun. Penguin Books. ISBN 1-88190141-6.
- Pitrè, Giuseppe (2004). Grammatica Siciliana. Edizioni Clio.
- Privitera, Joseph (1998). Beginner's Sicilian. Hippocrene. ISBN 0781806402.
- Privitera, Joseph (2001). "I Nurmanni in Sicilia Pt II / The Normans in Sicily Pt II". Arba Sicula XXII (1&2): 148–157.
- Privitera, Joseph (2004). Sicilian: The Oldest Romance Language. Legas. ISBN 0-14-015212-1.
- Ruffino, Giovanni (2001). Sicilia. Editori Laterza. ISBN 88-421-0582-1.
- Runciman, Steven (1958). The Sicilian Vespers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-43774-1.
- Zingarelli, Nicola (2006) (in Italian). Lo Zingarelli 2007. Vocabolario della lingua italiana. Con CD-ROM. Zanichelli. ISBN 8808042294.
External links
- (Sicilian) www.linguasiciliana.org
- (Italian) www.linguasiciliana.it
- Arba Sicula A non-profit organisation dedicated to preserving the Sicilian language
- Ethnologue report on Sicilian
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
